EIP-7702 : A New Era in Account Abstraction
Discover how EIP-7702 brings a new era of account abstraction, enabling Ethereum EOAs to act like smart contracts in the Pectra upgrade.

Introduction
Ethereum's account system has remained largely unchanged since its inception, consisting of two distinct account types: Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) controlled by private keys and Contract Accounts governed by smart contract code. While this design has served Ethereum well, it has created significant barriers to user experience improvements and mainstream adoption. EIP-7702, introduced by Vitalik Buterin and other Ethereum core developers in May 2024, represents a paradigm shift that bridges this gap by allowing EOAs to adopt smart contract functionality temporarily.
This revolutionary proposal introduces a new transaction type (0x04) that enables EOAs to delegate their execution to smart contracts while maintaining their original address and identity. By doing so, EIP-7702 unlocks advanced features like transaction batching, gas sponsorship, and programmable account logic without requiring users to migrate to entirely new wallet infrastructure.
Why is this EIP Needed
The current state of Ethereum's account system presents several critical limitations that hinder widespread adoption and user experience improvements:
Current Limitations of EOAs
- Single Transaction Restriction: EOAs can only execute one operation per transaction, leading to inefficient workflows. For example, interacting with a decentralized exchange requires separate transactions for token approval and the actual swap, resulting in higher gas costs and a poor user experience.
- Gas Payment Inflexibility: Users must hold ETH to pay for gas fees, creating barriers for newcomers who may only hold other tokens or prefer different payment methods.
- Limited Security Options: EOAs rely solely on private key security, with no built-in recovery mechanisms, multi-signature capabilities, or permission systems.
- Poor Onboarding Experience: New users face complex wallet setup processes, seed phrase management, and technical concepts that discourage adoption.
The Smart Contract Wallet Problem
While smart contract wallets exist and offer advanced features, they come with their challenges:
- Deployment Costs: Each user needs to deploy their smart contract wallet, incurring significant gas fees
- Compatibility Issues: Many dApps and services are optimized for EOAs and may not work seamlessly with smart contract wallets
- Fragmentation: Different smart contract wallet implementations create ecosystem fragmentation
EIP-7702 addresses these issues by allowing existing EOAs to gain smart contract capabilities without the overhead of deploying new contracts or changing addresses.
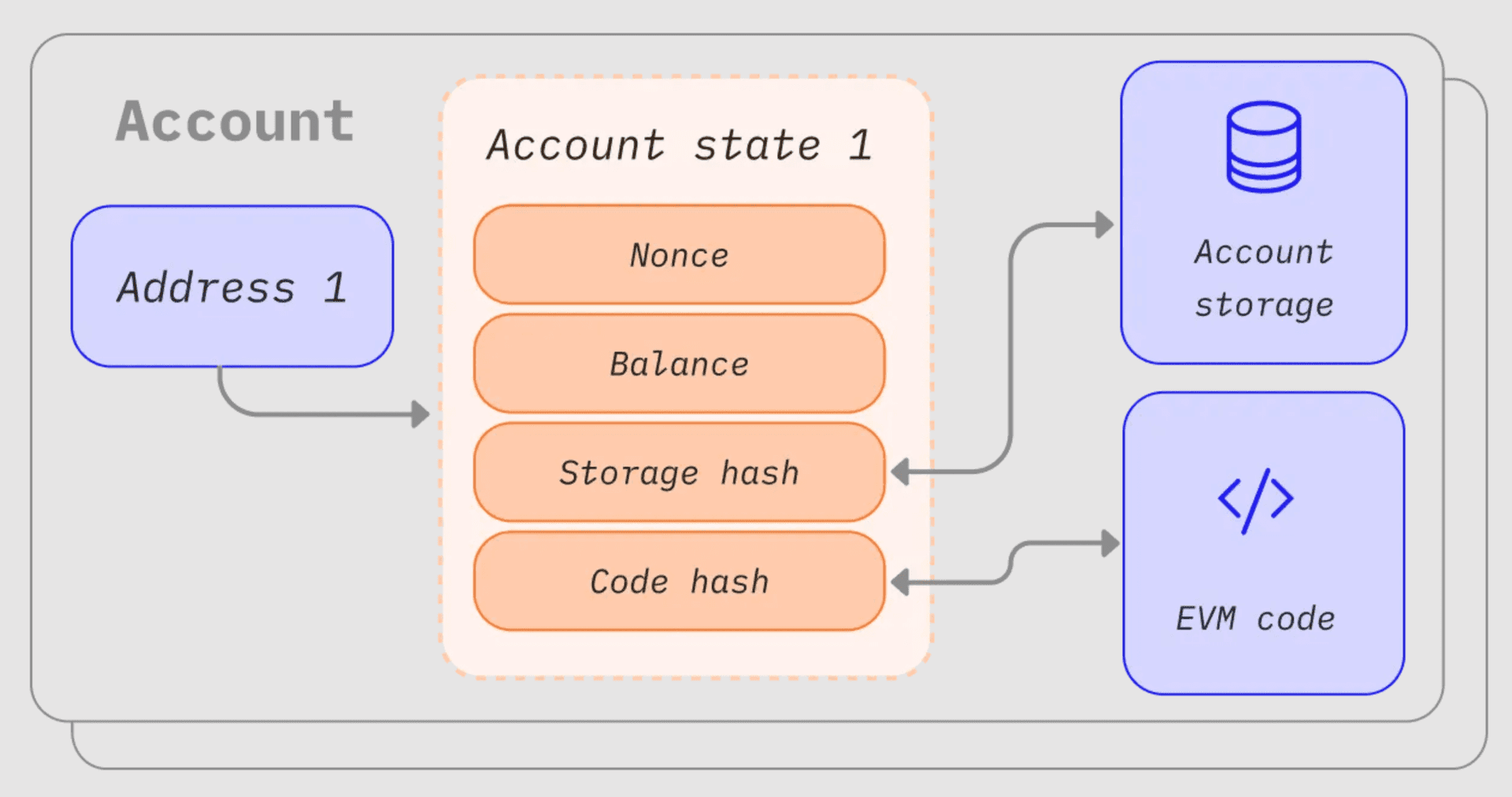
Understanding Account Types in the EVM
To fully appreciate EIP-7702's innovation, it's essential to understand how Ethereum's account system currently works:
| Category | Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) | Smart Contract Accounts |
| Structure |
|
|
| Capabilities |
|
|
| Limitations |
|
|
EIP-7702 creates a bridge between these two account types by allowing EOAs to temporarily "delegate" their execution to smart contracts. This delegation is achieved through a special delegation indicator (0xef0100 || address) that tells the EVM to execute the code at the specified address whenever the EOA is called
How EIP7702 Works
The Delegation Mechanism
The core innovation of EIP-7702 lies in its delegation system, which works through the following process:
- Authorization Creation
Users create authorization tuples containing:
1[chain_id, address, nonce, y_parity, r, s]Where:
- chain_id: The blockchain network identifier (0 for universal, or specific chain ID)
- address: The smart contract address to delegate to
- nonce: The current nonce of the authorizing account
- y_parity, r, s: Cryptographic signature components after signing this tuple.
- Transaction Structure
EIP-7702 introduces a new transaction type (0x04) with the following structure:
1[chain_id, nonce, max_priority_fee_per_gas, max_fee_per_gas,
2 gas_limit, destination, value, data, access_list,
3 authorization_list, signature_y_parity, signature_r, signature_s]The key addition is the authorization_list containing one or more authorization tuples.
- Processing Flow
When a Type 4 transaction is processed:
- Validation: Each authorization tuple is validated for signature correctness and nonce matching
- Code Setting: A delegation indicator
0xef0100 || addressis written to the authorizing account's code field - Execution: Future calls to the delegated account execute the smart contract code at the specified address
- Context Preservation: The
msg.senderremains the original EOA address during execution
- Delegation Indicator
The delegation indicator uses the banned opcode 0xef (from EIP-3541) followed by 0x0100 and the 20-byte contract address. This indicator tells the EVM that the account has delegated its execution to another contract.
Gas Costs and Economics
EIP-7702 introduces specific gas costs for delegation operations:
- PER_AUTH_BASE_COST: 12,500 gas per authorization tuple
- PER_EMPTY_ACCOUNT_COST: 25,000 gas if the account doesn't exist
- Cold Account Access: Additional 2,600 gas for first-time access to delegated contracts
These costs are designed to prevent spam while keeping delegation affordable for legitimate use cases.
Key Use Cases
- Transaction Batching: Combine multiple actions into one atomic transaction.
- Gas Sponsorship & Flexible Payments: Enable third-party gas payments or ERC-20 fee options.
- Permission Management: Create sub-keys with limited, role-specific permissions.
- Social Recovery: Recover accounts using guardians, MFA, or time delays.
- Session Keys & Automation: Use temporary keys for trusted automation and seamless UX.
EIP-7702 enables any EOA to function as a smart account, bringing account abstraction features without modifying the EVM core. By simplifying transactions, enhancing security, and offering greater flexibility, it improves usability and represents a significant step toward mainstream Ethereum adoption.
Future-Proof Your Ethereum Protocol with QuillAudits
Future-Proof Your Ethereum Protocol with QuillAudits
EIP-7702 brings powerful features to EOAs, but also new risks. QuillAudits secures your smart contracts and account abstraction implementations, helping you build confidently with a trusted Web3 security partner.
Security & Threat Considerations
- Delegate Contract Risks – Poorly designed delegate contracts can expose accounts to replay attacks, gas griefing, or unauthorized transfers. To prevent this, critical fields like nonce, gas, value, and target must be included in the signed data.
- Initialization Issues – Unlike normal smart contracts, 7702 accounts skip the usual storage initialization. This opens front-running risks during setup. Wallets should enforce signature checks (
ecrecover) to ensure only the account owner controls initialization. - Storage Collisions – Switching between delegate contracts can cause overlapping storage layouts. Developers should use structured patterns (e.g., ERC-7201) or clear state before migration to avoid unintended behavior.
tx.originConcerns – Delegated code can mislead checks relying ontx.origin, weakening protections like reentrancy guards. Developers should avoid usingtx.originin security logic.- Relayer Exploits – Relayers handling sponsored transactions risk griefing if accounts can revoke payloads or drain balances. Bond mechanisms or reputation systems can help mitigate this.
- Transaction Propagation – Delegation changes the usual behavior of EOAs, creating risks of stale or conflicting transactions. Clients should limit delegated EOAs to one pending transaction at a time or use account hydration strategies to maintain reliability.
Practical Example
1const { Wallet, JsonRpcProvider, Contract } = require("ethers");
2
3const RPC_URL = "<https://sepolia.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_PROJECT_ID>"; // replace with your Infura project ID
4const AUTHORITY_PRIVKEY = "YOUR_EOA_PRIVATE_KEY"; // replace with private key of EOA whose delegation you’re setting
5const DELEGATION_ADDRESS = "0xd08F5a5226622EB7275d5Fd045E80C0789F6a307"; // the address to delegate to aka contract address
6
7const provider = new JsonRpcProvider(RPC_URL, "sepolia");
8const authority = new Wallet(AUTHORITY_PRIVKEY, provider);
9
10// HelloWorld ABI
11const helloAbi = ["function ping() external pure returns (string memory)"];
12
13async function main() {
14 // get current nonce of the authority aka EOA
15 const nextTxNonce = await provider.getTransactionCount(
16 await authority.getAddress()
17 );
18
19 // Step 1: prepare 7702 authorization
20 const authReq = await authority.populateAuthorization({
21 address: DELEGATION_ADDRESS,
22 nonce: nextTxNonce + 1,
23 });
24 const authorization = await authority.authorize(authReq);
25
26 // Step 2: send transaction with authorizationList
27 const tx = await authority.sendTransaction({
28 to: "0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000",
29 authorizationList: [authorization],
30 });
31
32 console.log("Sent 7702 tx:", tx.hash);
33 const receipt = await tx.wait();
34 console.log(
35 "Mined in block:",
36 receipt.blockNumber,
37 "status:",
38 receipt.status
39 );
40
41 // Step 3: check your account code
42 const code = await provider.getCode(await authority.getAddress());
43 console.log("EOA code now:", code); // should be 0xef0100...<delegation_address>
44
45 //Step 4: check the contract call through authroity
46 const authorityAsContract = new Contract(
47 authority.address,
48 helloAbi,
49 provider
50 );
51
52 const result = await authorityAsContract.connect(authority).ping();
53 console.log("ping() result via delegation:", result);
54}
55
56main().catch((e) => {
57 console.error(e);
58 process.exit(1);
59});
Running the Script
1npm i ethers1node FILE_NAME.js
Example Output
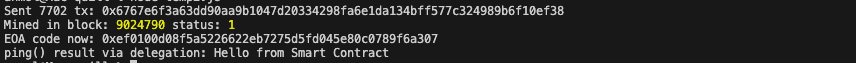
Conclusion
EIP-7702 represents a significant advancement in Ethereum’s account architecture, enabling Externally Owned Accounts to seamlessly access smart contract functionality. This proposal addresses long-standing limitations around transaction efficiency, gas flexibility, and account security, while maintaining compatibility with the existing ecosystem. Although it introduces new security considerations, EIP-7702 lays the foundation for a more user-friendly and resilient Ethereum. To ensure your protocol remains secure as the ecosystem evolves, explore our Ethereum Smart Contract Audit services. For more insights on securing Web3 projects, visit QuillAudits.
Contents



