New Gold Protocol Suffers $2M Flash Loan Breach
Flash loan breach hits New Gold Protocol, resulting in a $2M loss. Attackers exploited contract vulnerabilities for rapid, uncollateralized profit.

On September 17, 2025, the NewGold Protocol (NGP), a DeFi project on the BNB Chain, suffered a major exploit resulting in the loss of approximately $2 million in user funds. Launched with promises of "DeFi 3.0" innovation and sustainability, NGP emphasized security as "non-negotiable." However, the attack exposed critical vulnerabilities in its smart contract design, including reliance on a manipulable price oracle and flawed transfer logic. The exploit involved flash loan manipulation, leading to the drainage of liquidity pools and a subsequent 88% crash in the NGP token price.
Hack Analysis
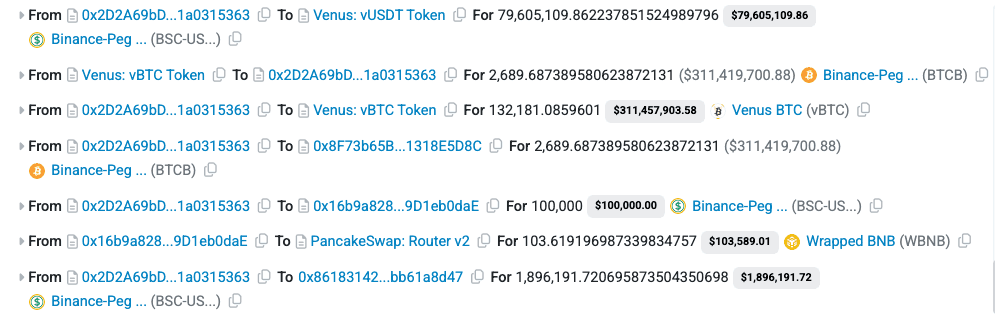
The attacker initially acquired NGP tokens across multiple EOAs by swapping funds on PancakeSwap. These funds were originally sourced through Tornado Cash.

The attacker then took out a BTCB flash loan via Moolah and used it as collateral on Venus Protocol to borrow vUSDT.
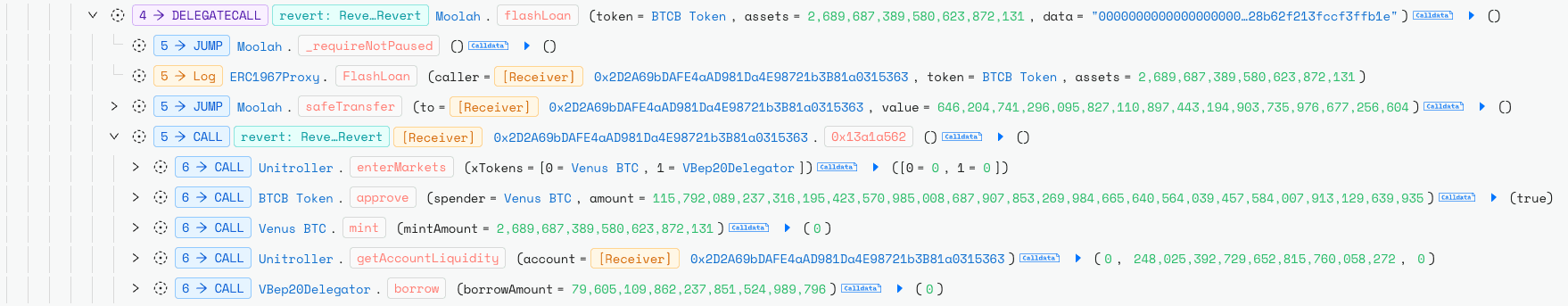
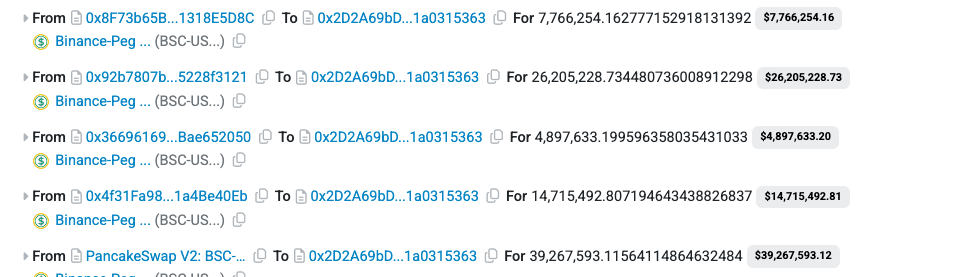
Next, the attacker executed multiple flash loans of BSC-USD from PancakeSwap, drawing liquidity from different pairs.
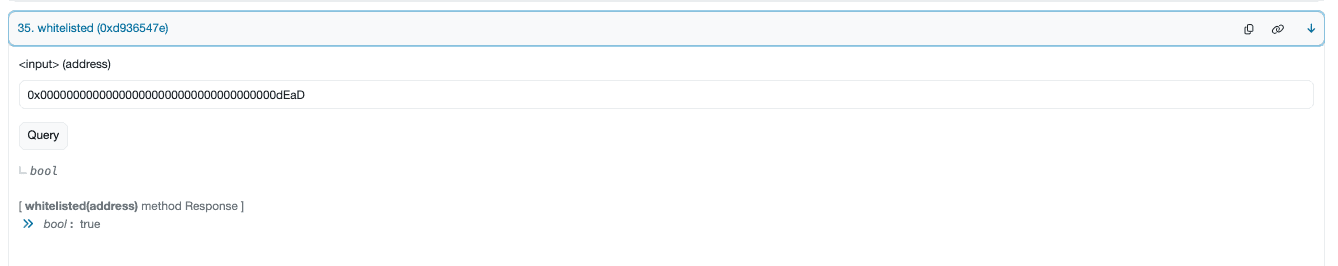
Using these funds, the attacker swapped BSC-USD for NGP in the PancakeSwap pool, but set the recipient address as the dead wallet. Since the dead wallet was whitelisted in the NGP protocol, this allowed the attacker to bypass the maxBuyAmountUsdt restriction.
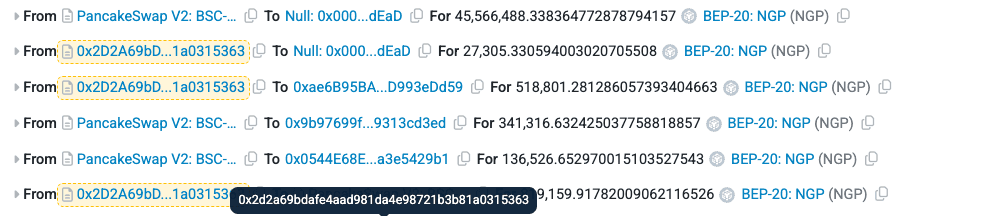

Within the NGP protocol, when tokens are sold, a 35% transaction fee is applied. Instead of deducting tokens from the seller’s balance and transferring the remainder, the protocol directly reduces tokens from the liquidity pool and then syncs the pool. This design flaw significantly diminished available liquidity.

Exploiting this vulnerability, the attacker used their initially acquired NGP tokens to perform a relatively small swap, which nevertheless drained the entire BSC-USD liquidity from the pool. After repaying all borrowed assets, the attacker walked away with approximately $2M in profit.
Root Cause
The exploit stemmed from two primary vulnerabilities in the NGP smart contract:
- Vulnerable Price Oracle: The
getPrice()function relied exclusively on PancakeSwap pool reserves without integrating external oracles (e.g., Chainlink) or safeguards against manipulation. This made it susceptible to flash loan attacks that temporarily altered pool balances.
- Flawed Fee and Transfer Mechanism: The 35% sales fee was deducted directly from the pool's balance rather than from the transferred amount, combined with a
sync()Call that the updated reserves post-deduction. This created a self-destructive loop when exploited with manipulated reserves, leading to pool depletion.
These issues highlight inadequate threat modeling and a lack of robust Oracle integration in the protocol's design.
Don’t Let Weak Oracles Drain Your Protocol!
Don’t Let Weak Oracles Drain Your Protocol!
The $2M NewGold exploit shows the risk of weak oracles. QuillAudits helps secure price feeds, logic, and defenses against flash loan attacks.
Relevant Address and Transactions
- Attacker EOAs:
- Malicious Contract: 0x2D2A69bDAFE4aAD981Da4E98721b3B81a0315363
- Attack Transaction:
0xc2066e0dff1a8a042057387d7356ad7ced76ab90904baa1e0b5ecbc2434df8e1
- NGP Token Contract: 0xd2F26200cD524dB097Cf4ab7cC2E5C38aB6ae5c9
Funds Flow After Attack
The attacker first exchanged the stolen BSC-USD for ETH through KyberSwap, effectively converting the compromised funds into a more liquid and widely used asset.
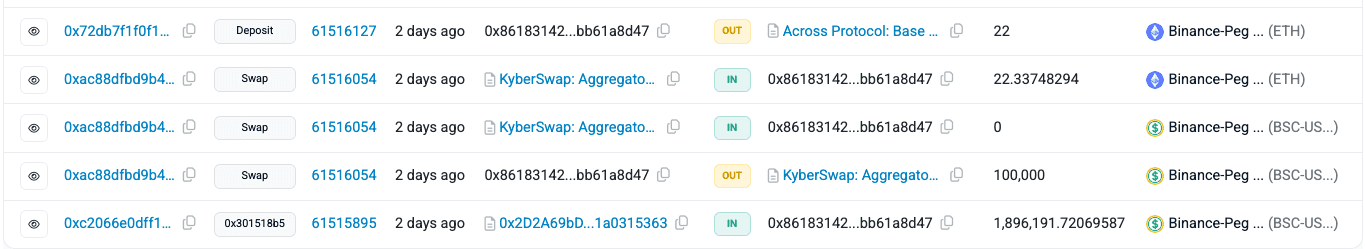
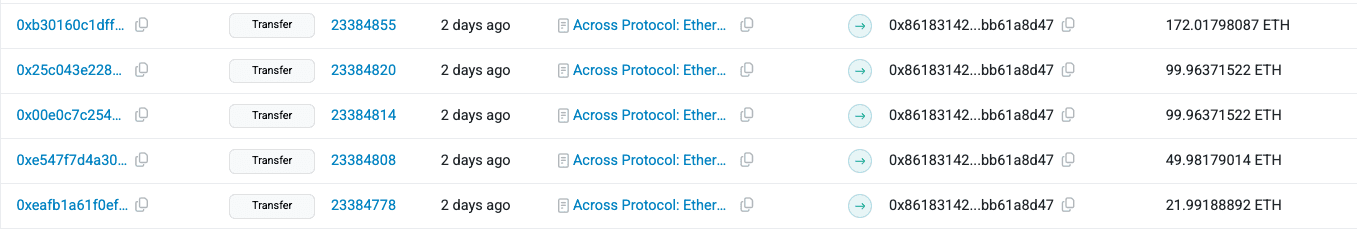
Next, the attacker bridged the newly acquired ETH from the BNB Chain to the Ethereum mainnet using the Across protocol, moving assets across chains to obscure the trail.
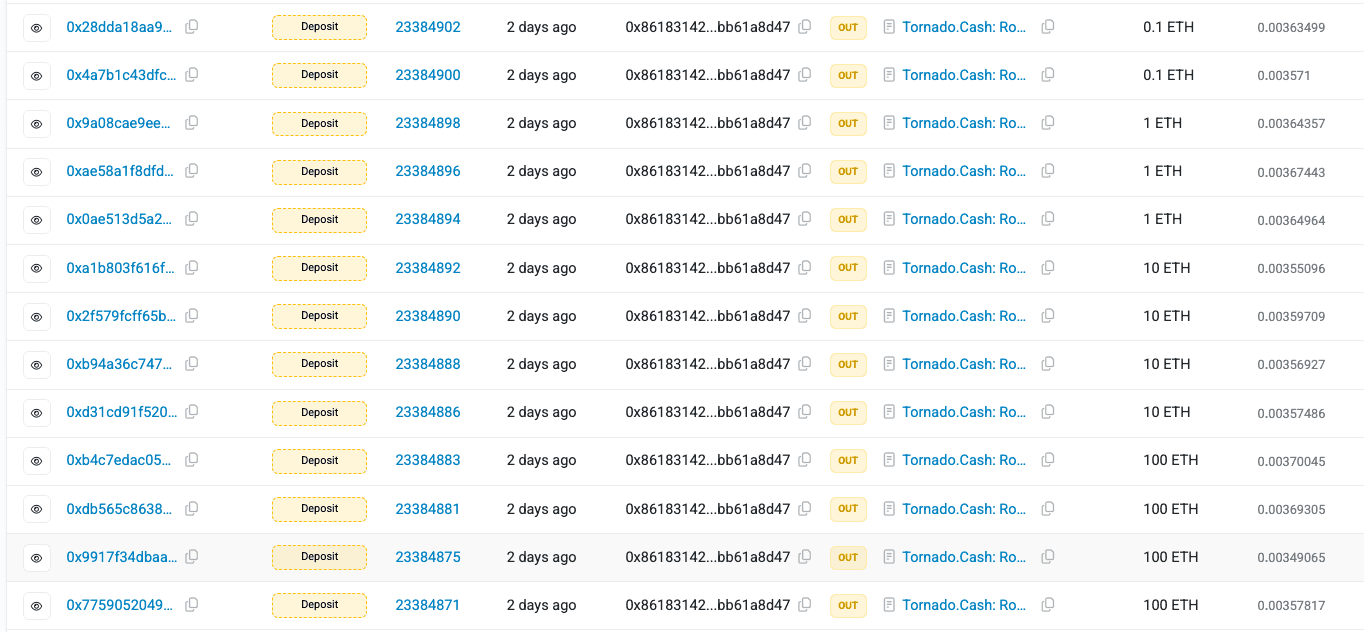
Finally, the attacker laundered the bridged ETH through Tornado Cash, leveraging the mixer’s anonymity features to conceal transaction history and make tracing the funds significantly more difficult.
Post Attack Mitigation
Following the exploit, the NewGold Protocol team acknowledged the incident in a public statement on September 20, 2025, expressing their intent to continue the project and work toward a relaunch.
However, no concrete measures or recovery assistance, such as contract actions, audits, or restitution plans, have been provided. Users remain without clear guidance, and trading continues to be affected due to the drained liquidity.
Conclusion
The NewGold Protocol exploit underscores the persistent risks in DeFi projects, particularly those relying on single-source price oracles and untested fee mechanisms. This incident resulted in a $2 million loss and eroded user trust due to the team's lack of response. To prevent similar vulnerabilities, protocols should integrate multi-source oracles, implement flash loan protections (e.g., time-weighted average prices), and conduct thorough smart contract audits. The attack serves as a reminder of the importance of robust design and transparent post-incident handling in the DeFi ecosystem.
Contents



