How To Audit a Smart Contract?
Looking for a smart contract audit? Explore real-world case studies, best practices, platform-specific guidance, and more

Introduction
Smart contracts are the powerhouse of blockchain technology. They are code stored on a blockchain, executing when specific conditions are fulfilled. After completion, transactions are traceable and cannot be reversed. They automate agreements, ensuring instant certainty for participants without intermediaries or delays. Additionally, they can automate a workflow only to move forward when certain criteria are met.
Smart contracts have transformed the blockchain space by enabling powerful decentralized applications, even in traditionally risk-averse sectors. However, they still pose major security risks. Many of the vulnerabilities in DeFi aren’t due to sophisticated hackers but stem from flaws in the smart contracts themselves.
In fact, over $2.3 billion in digital assets were exploited in just the first half of 2025, according to our latest Crypto Exploits H1 Report 2025, with smart contract vulnerabilities continuing to be the primary attack vector.
Smart contract audits play a critical role in blockchain risk management. By thoroughly reviewing and testing smart contracts, audits identify vulnerabilities and ensure code reliability. Complex smart contracts and high stakes make thorough audits essential, ensuring trust in blockchain systems for stakeholders and users.
What is a Smart Contract Audit?
Smart contract audits involve reviewing contract’s code to identify security flaws and errors, ensuring the reliability and security of blockchain applications. This process is crucial because smart contracts function strictly as written, without room for post-deployment corrections, making early error detection vital.
Smart contract audit service offers several advantages:
- Smart contract audit services offer several advantages:
- A security audit identifies project weaknesses, preventing costly errors and ensuring early detection of flaws post-release.
- Building trust is essential with both users and investors. An audit gives your project an extra layer of protection by serving as a security stamp.
- Security audits are essential for creating risk assessment plans and mitigation strategies for businesses handling private and sensitive information about individuals.
- An audit strengthens your project, builds a defense against attacks, and optimizes code performance for improved functionality.
Why are Smart Contract Security Audits Important?
Although blockchain technology itself is secure, blockchain applications may still contain security vulnerabilities.One of the biggest security incidents involving smart contract vulnerability was a theft worth $611m in 2021. The POLY NETWORK on BNB Chain was compromised. It was a Smart Contracts Vulnerability that led to a loss of $611.0M. To reduce these risks, a smart contract security audit team can be useful.
Code audits are crucial for all apps, but even more so for decentralized ones due to blockchain immutability. User funds cannot be recovered if they are lost due to a code vulnerability. Up to now, hackers have stolen over $5.79 billion from DeFi and a total of $7.65 billion from web3 DApps.

Smart contracts lacking audits risk legal issues like security flaws, regulatory breaches, and contract disputes. Unaudited contracts may contain exploitable flaws, risking financial loss and liability for developers. Ignoring regulations may lead to fines and legal trouble, while unclear contract code can spark enforcement issues. Unaudited contracts may violate consumer protection laws, inviting legal scrutiny. Parties must prioritize thorough auditing to minimize legal risks.
Major Security Breaches and DeFi Losses due to Smart contract Vulnerability :-
| Name | Amount loss | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Lendf.me (2020) | $25.0M | Incompatibility between ERC777 & DeFi smart contracts |
| POLY NETWORK (2021) | $611M | Access Control Exploit |
| BSC Token Hub Bridge (2022) | $570M | Proof Verifier Bug |
| Euler Finance (2023) | $197M | Flashloan Donate Function |
| Parity Multisig (2017) | $150M | Contract not initialized |
| Mirror Protocol | $90M | Duplicate Call Exploit |
Secure Your Smart Contracts with QuillAudits
Secure Your Smart Contracts with QuillAudits
Ready to secure your smart contracts? Take the first step towards a safer blockchain journey. Request an Audit with QuillAudits today & ensure your contracts are robust and secure!
Discover and learn more about such attacks on smart contracts vulnerabilities with QuillMonitor.
Businesses worry about smart contract deployment's irreversibility and security flaws, prompting the need for auditing:
1. Avoid errors: Early code audits prevent costly mistakes post-launch.
2. Expert review: Experienced auditors manually double-check code for accuracy.
3. Prevent attacks: Continuous monitoring detects and prevents security breaches.
4. Enhanced security: Audits assure decentralized product owners of code security.
5. Continuous assessment: Ongoing audits improve the development environment.
6. Analytical reports: Vulnerability reports offer executive summaries, details, and mitigation advice
Common Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Here are some of the common vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
Reentrancy Issues:- A reentrancy attack may happen when a smart contract function interacts with an untrusted external contract, allowing it to exploit vulnerabilities and potentially drain user funds.
Rounding Off Issue:- The rounding off Issue in smart contracts refers to a vulnerability that arises from improperly handling non-whole numbers, leading to unexpected results due to rounding errors. A notable example is the Radiant Capital Hack on January 3, 2023, resulting in a $4.5 million loss.
Frontrunning Opportunities:- Inadequately structured code in dApps can accidentally disclose forthcoming transaction data. Users can exploit this to secure profits, a disadvantage to the protocol.
Function visibility:- These errors occur when functions meant to be private are mistakenly defined as public. This allows anyone to access the function.
External Calls to Arbitrary Addresses:- Fraudulent contracts could withdraw funds when prompted by external calls to random addresses, leading to fund loss. Attackers exploit this flaw to execute unauthorized actions, potentially disrupting the contract's functionality.
Inconsistent Data:- There can be several problems when smart contract functions use data without the necessary validation. Incorrect contract execution due to inaccurate data could have negative effects or financial losses.
How to Audit a Smart Contract: Different Phases of the Process
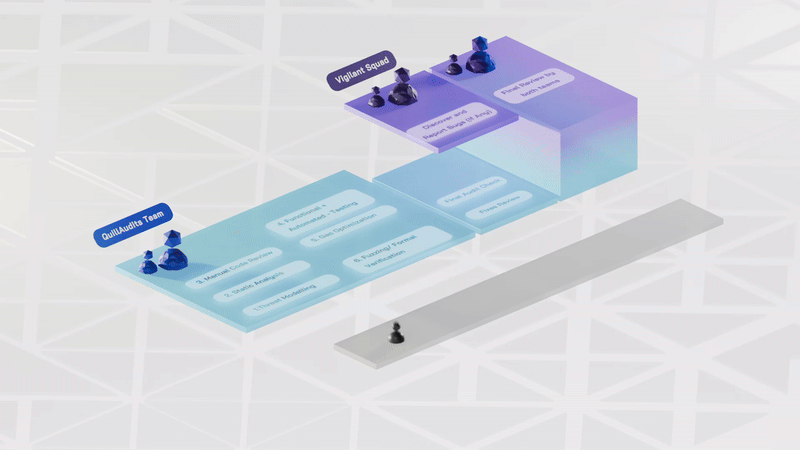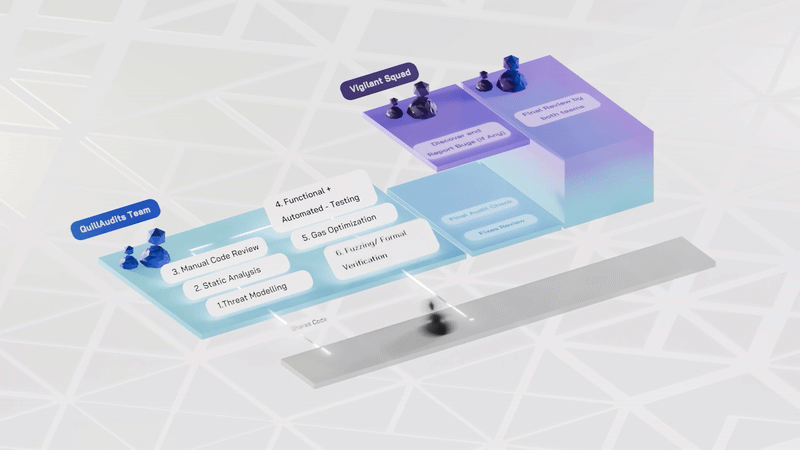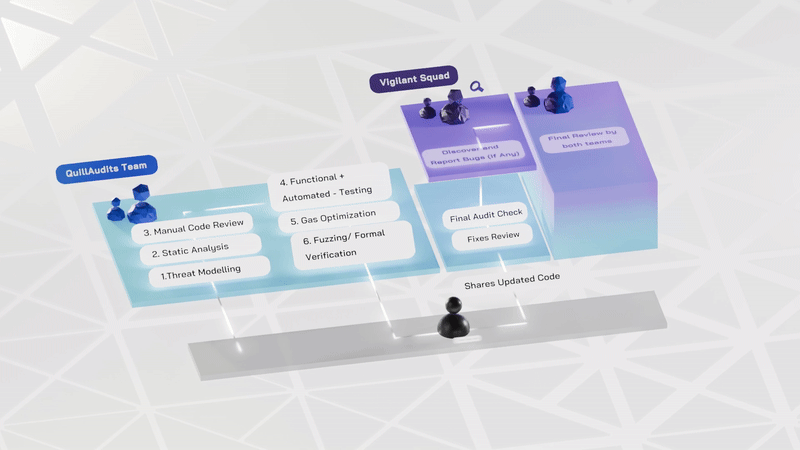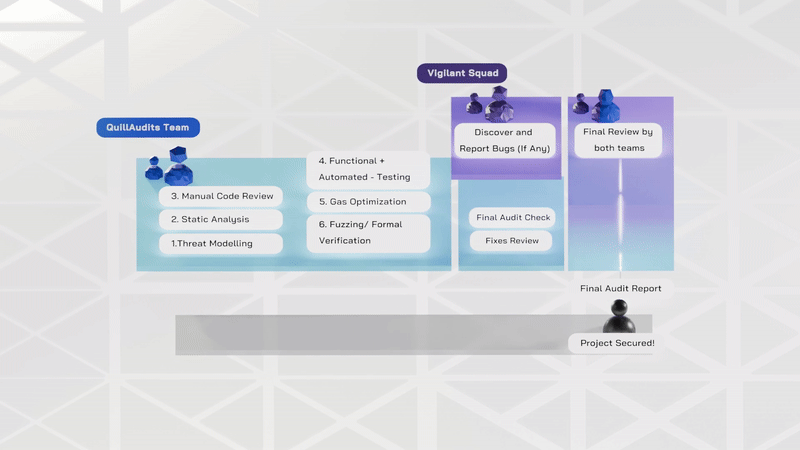
Smart contract audits follow structured phases to identify and address vulnerabilities effectively. Here's an overview of each Phase and its significance:
1. Pre-audit Phase:- This Phase establishes the audit's foundation by grasping the project's objectives, structure, and smart contract functionalities. It ensures that auditors and developers understand the project's scope, goals, and potential areas of concern.
2. Manual Review:- In this Phase, manual Review ensures the contract aligns with specifications. It checks for common security vulnerabilities. The goal is to engage skilled reviewers for a thorough examination.
3. Manual Testing:- Smart contract will be manually deployed on any of the test networks (Ropsten / Rinkeby) using remix IDE. All the transaction hashes will be recorded. Gas consumption and the behavior of functions are also noted.
4. Functional Testing:- The smart contract is deployed in a sandbox environment like testnet / mainnet forks, hardhat, ganache, etc. Functions are tested thoroughly for intended functionality and performance. Verification ensures intended behavior and optimal gas consumption. Gas limits of functions are verified for efficiency.
5.Automated Review and Testing:- During this stage, auditors utilize advanced tools such as QuillShield and Slither, to scrutinize and analyze contract codes. The focus is on uncovering risks like security vulnerabilities, bugs, syntax errors, and weak code.
6. Initial audit report submission:- After thorough inspection, auditors submit an initial audit report detailing findings and recommendations for fixes.
7. Final Audit Report Submission: After the initial audit fixes, the process is repeated, and the final audit report is delivered.
Classification of code errors

Real-world Case Studies in Smart Contract Auditing
- Uniswap V2 Reentrancy Bug :- In 2020, a reentrancy glitch was found in Uniswap V2, a decentralized exchange protocol.This incident underscored the crucial function of auditors in detecting and addressing intricate vulnerabilities, even within established projects. It emphasized understanding smart contracts and thorough security checks to uncover potential weaknesses.
- The DAO Hack :- 2016’s The DAO hack served as a pivotal moment for smart contract auditing. The breach let an attacker steal millions from The DAO, underscoring the need for meticulous audits.
- Carpe Diem Pension (CDP) :- The CDP protocol comprises Pension, Auction, and CDPtoken contracts. CDP tokens can be deposited in the Pension contract for rewards. QuillAudits discovered 33 issues, including logic errors and resource misallocation. The security audit fixed critical vulnerabilities, safeguarding user funds and platform stability.
Are there any tools for Auditing Smart Contracts ?
Here's a comprehensive overview of tools used in smart contract audits:
1. QuillShield :- QuillShield is a comprehensive Web3 security platform designed to support enterprises, developers, and communities. It offers a range of security solutions from development to post-deployment.
- Development to deployment coverage: Offers security solutions throughout the entire Web3 project lifecycle.
- Proactive threat detection: Features include audits, scans, simulators, optimizers, and automated audits.
- AI-powered threat intelligence: Utilizes AI and threat intelligence to provide on-chain monitoring, event alerts, and forensic analysis.
- Combatting fraud: Protects digital assets, smart contracts, and blockchain networks from fraudulent activities.
2. Vulndetector :- Vulndetector, a top-notch tool, excels in detecting vulnerabilities, offering precision and gas optimizations for streamlined performance. Here are some vulnerabilities detected by this powerful tool, showcasing its innovative approach to smart contract security:
- Unexpected Ether balance
- Functions of wstETH Utilize stETH Units Instead of Eth
- get_dy_underlying() lacks resistance to flash loans for pricing.
3. Mythril :- A framework for bug hunting that aids in finding potential vulnerabilities within Solidity smart contracts.
The Mythril tool can discover the following vulnerabilities:
- Transaction order dependency
- Random number
- Unchecked call
4. SmartCheck :- This tool looks for vulnerabilities in the source code of smart contracts using static analysis. SmartCheck evaluates Solidity code against XPath patterns after converting it into an XML-based intermediate representation.
It checks for :-
- Re-entrancy
- Unchecked external call
- Transfer forwards all gas
- DoS by external contract
5. ContractFuzzer :- ContractFuzzer utilizes this method to uncover vulnerabilities in Ethereum smart contracts, relying on their ABI specifications. It establishes test oracles, logs runtime behaviors, and analyzes logs for vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
The ContractFuzzer tool is capable of discovering the following vulnerabilities:
- Gasless Send
- Exception Disorder
- Block number dependency
- Dangerous delegateCall
6. Slither :- This static analysis tool reviews Solidity source code for security flaws and ensures adherence to industry best practices. Slither is capable of discovering the following vulnerabilities:
- Dangerous usage of tx.origin
- Selfdestruct functions
- Uninitialized state variables
Types of Smart Contract Audits

- Automated Audits: In this method, specialized software scans the contract’s code for known vulnerabilities. It functions like a spellchecker for common errors but may potentially miss more complex issues.
- Manual Audits: Experienced auditors perform manual audits by thoroughly examining all parts of the code. They think like hackers to spot potential security risks.
- Hybrid Audits: Hybrid audits combine automated checks for speed with manual review for insight. They provide a comprehensive examination, leveraging the strengths of both approaches.
- Comprehensive Audits: These audits provide a thorough evaluation of the code. They evaluate how the contract integrates into the system, ensuring seamless functioning, much like a health check-up.
- Limited Audits: Limited audits focus on essential contract aspects when time or resources are scarce. They resemble quick car services for critical systems.
- Continuous Audits: Continuous audits involve regular checks to ensure updates haven't introduced flaws. They act as everlasting security guards monitoring vulnerabilities.
How can one choose the Right Smart Contract Auditor
Selecting a smart contract auditor requires considering factors to ensure contract security and reliability.
- Past Audits and Report Quality: Review the auditor's previous audits and any security incidents their clients have encountered. Seek auditors offering clear, thorough audit reports detailing findings and recommendations.
- Portfolio and Expertise : Assess auditor's portfolio, review projects audited, handling of security incidents, and team's blockchain security expertise.
- Methodology and Tools: Understand the auditor's approach, including scope, tools, standards used , and whether they use automated testing and manual review.
- Customized Approach: Look for auditors adaptable to your project's needs, including budget and timing considerations. Look for additional services such as consultations or threat modeling if necessary.
- Cost and Price Structure: Consider auditors' pricing models: flat fees, hourly rates, or combinations. Assess included services like audit rounds. Prioritize value over price, considering potential costs of undiscovered vulnerabilities. Ensure auditors offer scalable services for growing projects.
When choosing a smart contract auditor, focus on expertise, responsiveness, and audit techniques. Quill Audits delivers swift responses and thorough audits across diverse blockchain platforms.
Beyond the Audit: Best Practices for Smart Contract Security
- Use Delegatecall Carefully :- Delegatecall acts like a message call but runs code at the target address within the caller's context, retaining msg.sender and msg.value. Delegatecall assists in creating libraries but poses risks due to dynamic code loading, possibly resulting in unexpected execution.
- Use Reentrancy Guard :- Reentrancy refers to a programming technique where the execution of a function temporarily halts due to an external function call. The external function can repeatedly call itself during a pause in its original execution. Unprotected external calls can drain a contract's funds through reentrancy unless mitigated.
- Use msg.sender Instead of tx.origin for Authentication :- In Solidity, tx.origin serves as a global variable that provides the address of the sender of a transaction. Depending on tx.origin for authorization risks contract exploitation if a trusted account interacts with a malicious one. Use msg.sender instead of tx.origin to reduce vulnerability to attacks. Msg.sender can be a contract or an externally owned account, unlike tx.origin, ensuring safer authentication.
- Avoid Block Timestamp Manipulation :- In the past, block timestamps have been useful for various things in smart contracts, like generating random numbers, locking funds for specific durations, and triggering time-based actions. However, there's a risk involved because miners can slightly adjust timestamps. Using block timestamps incorrectly can lead to problems in smart contracts. While you can estimate the time between events using block numbers and average block time, this method isn't ideal as block times can fluctuate and cause issues with functionality.
- Properly Use Solidity Visibility Modifiers :- Function visibility options in smart contracts include internal, external, private, and public modifiers. Here's a quick rundown:
- Public: Accessible by the main contract, derived contracts, and third-party contracts.
- External: Callable only by third-party contracts.
- Internal: Callable by the main contract and its derived contracts.
- Private: Only callable within the specifying main contract.
- Neglecting to specify a visibility modifier often leads to vulnerabilities, so functions default to public, potentially causing unintended state changes.

Check Out Our Work
We've audited top DApps and DeFi protocols, ensuring they remain secure and Free from Hacks. Check out their audit reports to see our impact.

Conclusion
Smart contract audits are crucial in blockchain, ensuring integrity, functionality, and durability. Irreversible transactions highlight a vital need for thorough audits, given the high stakes and losses from vulnerabilities.
Smart contract audits find and fix security issues, preventing errors and boosting blockchain app credibility with expert auditors and tools. Participants in the blockchain ecosystem must prioritize smart contract audits in project development. Using available resources, best practices, and professional auditing services reduces risk for successful blockchain solutions.
In the fast-evolving world of Web3 and DeFi, smart contract security is important. QuillAudits offers tailored auditing services for DeFi and Web3 ventures, securing $3 billion in assets. Trusted globally, we safeguard blockchain assets effectively. Ensure your project's security with a free audit consultation from QuillAudits today.
Contents



